8 3 Compute and Evaluate Labor Variances Principles of Accounting, Volume 2: Managerial Accounting
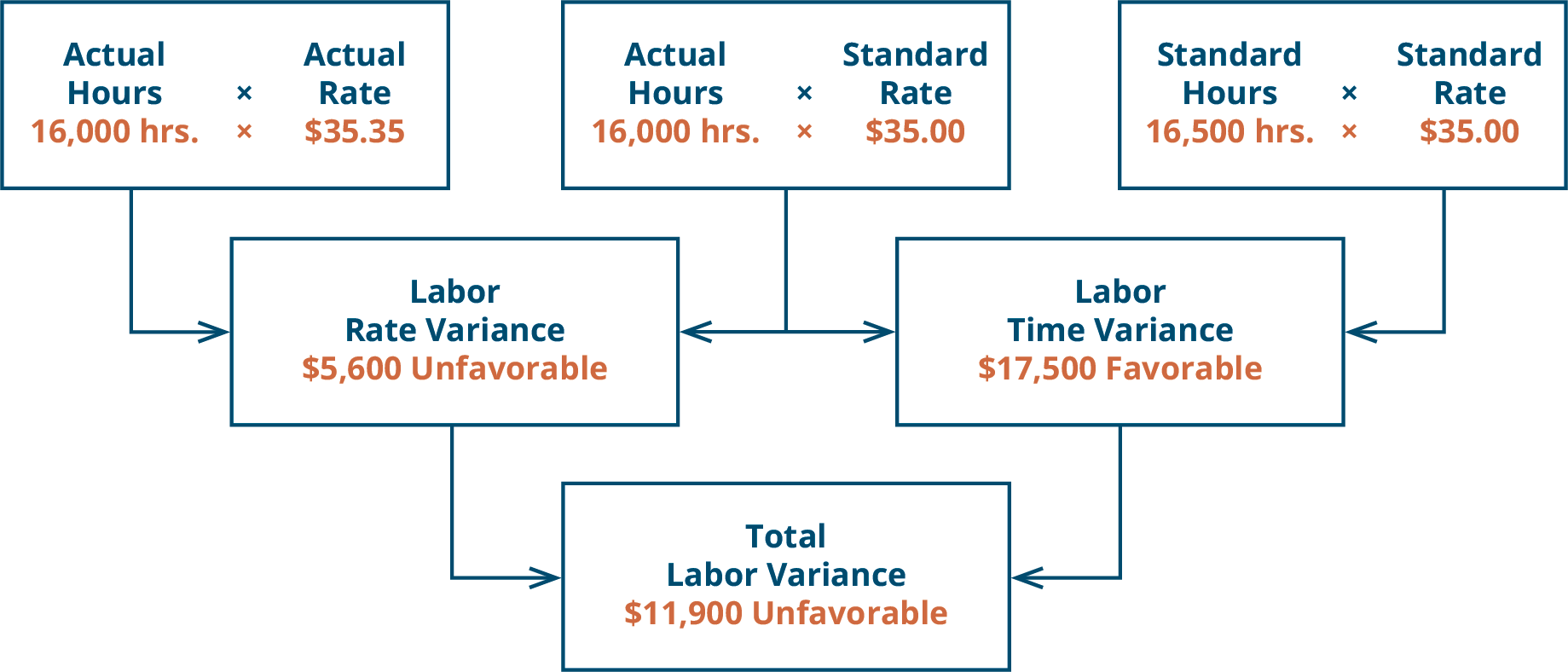
Figure 10.6 “Direct Labor Variance Analysis for Jerry’s Ice Cream” shows how to calculate the labor rate and efficiency variances given the actual results and standards information. Review this figure carefully before moving on to the next section where these calculations are explained in detail. The labor rate variance measures the difference between the actual and expected cost of labor. An unfavorable variance means that the cost of labor was more expensive than anticipated, while a favorable variance indicates that the cost of labor was less expensive than planned. This information can be used for planning purposes in the development of budgets for future periods, as well as a feedback loop back to those employees responsible for the direct labor component of a business. For example, the variance can be used to evaluate the performance of a company’s bargaining staff in setting hourly rates with the company union for the next contract period.
Direct Labor Variances
Suppose, for example, the standard time to manufacture a product is one hour but the product is completed in 1.15 hours, the variance in hours would be 0.15 hours – unfavorable. If the direct labor cost is $6.00 per hour, the variance in dollars would be $0.90 (0.15 hours × $6.00). For proper financial measurement, the variance is normally expressed in dollars rather than hours. Recall from Figure 10.1 “Standard Costs at Jerry’s Ice Cream” that the standard rate for Jerry’s is $13 per direct labor hour and the standard direct labor hours is 0.10 per unit.
Definition of Labor Efficiency Variance
Background Company A, a mid-sized manufacturing firm, experienced significant fluctuations in its labor costs over several quarters. Upon analyzing their financial statements, management identified a persistent unfavorable labor rate variance. Changes in the labor market, such as a shortage of skilled workers or new labor agreements, can lead to wage adjustments.
Submit to get your question answered.
Outcome These corrective actions resulted in a significant reduction in labor efficiency variance. Company B not only improved productivity but also saw a boost in employee morale as workers experienced fewer interruptions and delays in their tasks. Working conditions and employee morale play a significant role in labor efficiency.
Do you own a business?
In this case, the actual hours worked per box are 0.20, the standard hours per box are 0.10, and the standard rate per hour is $8.00. This is an unfavorable outcome because the actual hours worked were more than the standard hours expected per box. As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider retraining its workers, changing the production process to be more efficient, or increasing prices to cover labor costs. Direct labor rate variance is equal to the difference between actual hourly rate and standard hourly rate multiplied by the actual hours worked during the period.
The total actual cost direct labor cost was $1,550 lower than the standard cost, which is a favorable outcome. Hitech manufacturing company legal bookkeeping is highly labor intensive and uses standard costing system. The standard time to manufacture a product at Hitech is 2.5 direct labor hours.
If the outcome is unfavorable, the actual costs related to labor were more than the expected (standard) costs. If the outcome is favorable, the actual costs related to labor are less than the expected (standard) costs. The standard cost of direct labor and the variances for the February 2023 output is computed next. The following equations summarize the calculations for direct labor cost variance.
All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Mark P. Holtzman, PhD, CPA, is Chair of the Department of Accounting and Taxation at Seton Hall University.
- It measures the difference between the actual labor costs incurred during production and the standard labor costs that were expected or budgeted.
- In order to keep the overall direct labor cost inline with standards while maintaining the output quality, it is much important to assign right tasks to right workers.
- Companies should continuously monitor labor variances to ensure that labor costs remain aligned with budgeted expectations.
- Since this measures the performance of workers, it may be caused by worker deficiencies or by poor production methods.
Total actual and standard direct labor costs are calculated by multiplying number of hours by rate, and the results are shown in the last row of the first two columns. Understanding labor rate variance helps companies manage labor costs more effectively by identifying discrepancies between actual and standard wage rates. By analyzing these variances, businesses can take corrective actions to align their labor expenses with budgeted costs, ultimately improving financial performance and cost control. In this question, the company has experienced an unfavorable direct labor efficiency variance of $325 during March because its workers took more hours (1,850) than the hours allowed by standards (1,800) to complete 600 units. This information gives the management a way to monitor and control production costs. Next, we calculate and analyze variable manufacturing overhead cost variances.
Understanding labor efficiency variance helps companies identify inefficiencies in their production processes and take corrective actions to improve labor productivity. This results in a favorable labor efficiency variance of $3,000, indicating that the company used 200 fewer hours than expected, saving $3,000 in labor costs. This results in an unfavorable labor rate variance of $2,000, indicating that the company spent $2,000 more on labor than anticipated due to higher wage rates. Labour Rate Variance is the difference between the standard cost and the actual cost paid for the actual number of hours. If the total actual cost is higher than the total standard cost, the variance is unfavorable since the company paid more than what it expected to pay. The direct labor variance measures how efficiently the company uses labor as well as how effective it is at pricing labor.
The difference between the standard cost of direct labor and the actual hours of direct labor at standard rate equals the direct labor quantity variance. As with direct materials variances, all positive variances are unfavorable, and all negative variances are favorable. The labor rate variance calculation presented previously shows the actual rate paid for labor was $15 per hour and the standard rate was $13. This results in an unfavorable variance since the actual rate was higher than the expected (budgeted) rate. The DL rate variance is unfavorable if the actual rate per hour is higher than the standard rate. Though unfavorable, the variance may have a positive effect on the efficiency of production (favorable direct labor efficiency variance) or in the quality of the finished products.

